Exploring the Groin Vault in Architecture | Overview, Definition, Development, Forms, & Fascinating Facts
- Free 2024 Lesson
This short course about the Groin Vault is a thorough, free online resource that covers all aspects of groin vault architecture. Through this course, you'll gain an understanding of its history, design, and broad applications. We include interactive content and clear explanations to deepen your knowledge of architectural innovations.
Free online course: Explore the full history and potential of groin vaults in architecture, from ancient innovations to modern adaptations.
The Groin Vault: Exploring Architectural Mastery from Antiquity to Modernity
Origins and Evolution of Groin Vault Ceiling
groin vault architecture
Introduction: Unveiling the Groin Vault Ceiling
Discover the origins of the groin vault, starting from its ancient roots through to its development in Romanesque and Gothic architecture.
This course offers an in-depth look at groin vaults, essential architectural elements known for their historical significance and structural utility. We will explore how these vaults originated, how they have evolved over time, and their continuing impact on architectural design from ancient structures to contemporary buildings. Through this exploration, you'll learn about the technical aspects of groin vault construction and their role in the development of significant architectural styles.
Subsections:
- The Concept of the Groin Vault Ceiling: Definition and basic mechanics.
- Historical Development: From Roman engineering to medieval cathedrals.
- Technological Advancements: How innovations in materials and techniques facilitated the rise of groin vaults.
Construction Techniques: Step-by-step illustrations of how Romans constructed groin vaults, highlighting the use of materials like stone and concrete.
The Concept of the Groin Vault
Definition and Basic Mechanics
A groin vault is formed by the intersection of two barrel vaults at right angles to each other. This design creates a structural arch in three dimensions that effectively distributes weight down to the corners of the vault, reducing the need for extensive support walls or columns.
This method of construction allows for the creation of spacious interiors with more complex geometries. By distributing forces efficiently, groin vaults help maintain the integrity of the building while enabling larger and more open spaces. This architectural technique has been pivotal in the evolution of building design, providing both aesthetic beauty and functional benefits.
Visuals: Groin Vault Construction from Roman Times
For this section, we would include detailed diagrams that illustrate the construction of groin vaults during the Roman era. These visuals would provide clarity on the following aspects:
Basic Structure: A diagram showing the basic components of a groin vault, including the intersecting barrel vaults.
Basic Structure of Groin Vaults
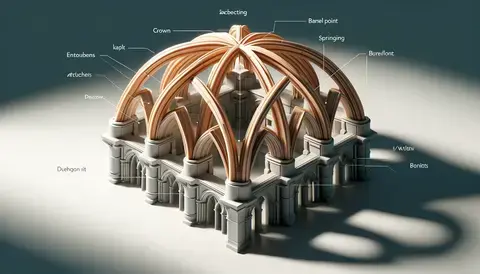
A groin vault is formed by the intersection of two barrel vaults at right angles. This structure is fundamental in creating arched ceilings that are both sturdy and aesthetically pleasing. Here’s a simple breakdown:
Barrel Vaults: These are continuous arches that extend along a given path, typically straight. When two such vaults cross each other, they form a groin vault.

Intersection: The point where the two barrel vaults meet is known as the groin. This intersection is crucial because it helps distribute the weight from the roof down to the columns or walls below, improving the structure's stability.

Components: The main components include the crown (the highest point of the vault), the groin (intersection point), and the springing (where the vault begins to curve upward from the support).
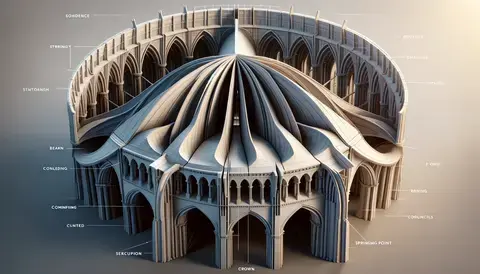
This basic structural setup allows groin vaults to support heavier loads than a simple flat ceiling or a single barrel vault, enabling the construction of larger and more open interior spaces without the need for many internal supports.
Historical Development: From Roman Engineering to Medieval Cathedrals
The evolution of groin vaults is a fascinating journey through architectural history, beginning with Roman engineering and culminating in the grandeur of medieval cathedrals. This development showcases not only advancements in construction techniques but also changes in aesthetic preferences and structural demands over the centuries.
Roman Beginnings
Groin vaults originated in the architecture of ancient Rome, where they were primarily used in the construction of large public buildings like bathhouses and aqueducts. The Romans favored groin vaults for their strength and ability to cover wide spaces without internal supports, facilitating larger and more open interiors.
Transition to Medieval Times
As architectural styles shifted with the fall of Rome, the knowledge and use of groin vaults persisted and evolved. By the medieval period, particularly during the Romanesque and Gothic eras, groin vaults had become a crucial element in the design of churches and cathedrals across Europe.
The Gothic Innovation
The Gothic period marked a significant evolution in the use of groin vaults. Architects pushed the boundaries of height and light in cathedral design, utilizing groin vaults to create taller, more expansive interiors that were filled with natural light. This was achieved through the innovative use of pointed arches and flying buttresses, which distributed the structural loads more effectively, allowing for higher walls and larger windows.
The transition from Roman practicality to medieval spirituality in architecture not only reflects changes in building technology but also shifts in cultural and religious values, illustrating how architectural forms can embody the spirit of their times. Groin vaults, in their evolution, tell a story of human ingenuity adapting to the needs and aspirations of different eras.
Technological Advancements: How Innovations in Materials and Techniques Facilitated the Rise of Groin Vaults
The advancement of groin vaults in architecture is closely linked to technological innovations in materials and construction techniques. These developments not only improved the structural capabilities of buildings but also expanded the creative possibilities for architects throughout history.
Innovations in Materials
Originally, groin vaults were constructed using stone or concrete, materials that were readily available to the Romans and known for their durability and strength. Over time, the introduction of new materials such as brick and later, reinforced concrete, allowed for more flexibility in vault designs and the ability to span larger distances without the risk of collapse.
Improved Masonry Techniques
The craft of masonry saw significant advances between the Roman period and the Middle Ages. Improved tools and techniques allowed builders to achieve tighter and more precise fits between stones, crucial for the integrity of arches in groin vaults. This precision in masonry was vital for the construction of the more complex designs seen in Gothic cathedrals.
The Role of Engineering Tools
The development of engineering tools such as the compass and more sophisticated leveling devices enabled architects to plan and execute more complex vault structures. These tools ensured greater accuracy in the curvature of arches and the overall symmetry of the vaults, essential components in achieving the desired aesthetics and functionality.
Experimentation with Geometric Forms
Advancements in understanding geometry allowed architects to experiment with different shapes and intersections of vaults. This experimentation led to the development of ribbed vaults, which are a type of groin vault enhanced with projecting stonework ribs. These ribs added both structural support and decorative elements, pushing the boundaries of what could be achieved with groin vault constructions.
These technological advancements not only made groin vaults more practical and efficient but also transformed them into expressions of artistic achievement. By leveraging new materials and improved techniques, architects were able to take groin vaults to new heights, literally and figuratively, culminating in the awe-inspiring spaces of medieval cathedrals.
Construction Techniques of Groin Vault Ceiling
Construction Techniques: Step-by-step illustrations of how Romans constructed groin vaults, highlighting the use of materials like stone and concrete.
Construction Techniques of Roman Groin Vaults
To illustrate the Roman techniques used in constructing groin vaults, a series of step-by-step visuals would be ideal. This image show each phase of the construction process, emphasizing the materials and methods specific to the Roman era.

Step 1: Base Preparation
A foundation of stone or compacted earth is laid down to establish a stable base for the vault.
Step 2: Support Framework Erection
A temporary wooden framework, known as centering, is assembled to provide support for the stones of the vault during construction, ensuring the arches maintain their shape until the keystone is placed.
Step 3: Stone Placement
Specially shaped stones are placed along the framework, including voussoirs (wedge-shaped stones) for the arches and the keystone at the apex, which locks the other stones into place.
Step 4: Mortar Application
Mortar is applied between the stones to reinforce them, ensuring the stability and durability of the vault. The mortar must be sufficiently strong to hold the stones together once the centering is removed.
Step 5: Framework Removal
The wooden centering is taken away, marking a critical phase where the integrity of the vault is tested. If constructed correctly, the arches will remain firm, supporting themselves and any additional structures above.
Architectural Details:
Close-ups on the key architectural features of Roman groin vaults, such as the precise angles at which the barrel vaults intersect.
Architectural Details of Roman Groin Vaults
Key features that highlight the craftsmanship and engineering behind these structures, particularly emphasizing the precise angles at which the barrel vaults intersect:
Close-Up of Intersection Points
A detailed view of the intersection or groin, where the barrel vaults meet. The precise angles and the interlocking of the stones, which is critical for distributing the structural load evenly.
Detailing of Voussoirs and Keystone
A zoom in on the voussoirs (the wedge-shaped stones) and the keystone at the apex of the arch. This highlights the craftsmanship in shaping these stones to fit perfectly together, ensuring the stability and durability of the vault.
Surface Textures and Materials
The surface textures of the materials used, such as the quality of the stone or concrete to give a sense of the material properties that contributed to the longevity and strength of Roman constructions.

These detailed visuals would not only provide a deeper understanding of the construction techniques but also celebrate the aesthetic aspects of Roman groin vaults, showcasing the blend of functionality and artistry that characterizes much of Roman architecture.
Historical Examples: Groin Vault Origins
Diagrams of famous Roman buildings that employed groin vaults, demonstrating their practical application in public baths, aqueducts, and other infrastructure.
Here are four images showcasing historical examples of groin vaults in Roman architecture:
Roman Public Baths (Baths of Caracalla or Diocletian): This image depicts the complex interior layout of a typical Roman bath, highlighting the use of groin vaults to support large roof spaces and enhance thermal efficiency.
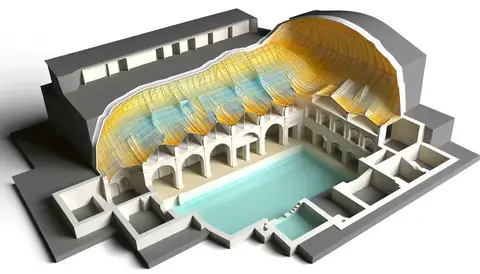
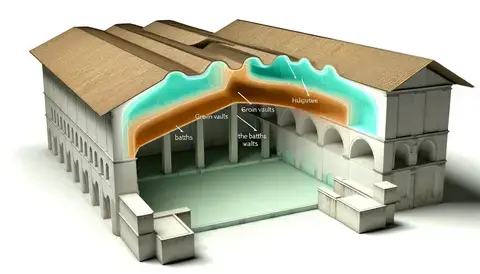
Roman Architecture: Roman Aqueduct (Aqua Claudia): This diagram shows a section of the aqueduct, focusing on the use of groin vaults to support the water channel over long distances, contributing to the structural stability of the aqueduct.

Roman Civic Building (Markets of Trajan): The image captures the architectural structure of the Markets of Trajan, illustrating how groin vaults were employed to create functional spaces within the multi-level commercial complex.

These images provide a realistic view of the architectural techniques and applications of groin vaults in various types of Roman infrastructure.
These visuals will not only help to visually communicate the mechanics and beauty of groin vaults but also connect learners to the historical context in which these structures were first developed and utilized.
Key Takeaways: Groin Vault Fundamentals and Initial Applications
Structural Efficiency: The groin vault is fundamentally designed to distribute weight evenly to the supporting walls or columns. This efficiency allows for larger and more open spaces within a structure, making it ideal for public buildings like baths and marketplaces in ancient times.
Architectural Versatility: The initial application of groin vaults during the Roman era demonstrated their versatility across various infrastructures, from aqueducts that spanned great distances to grand public baths and civic buildings. This adaptability shows the groin vault's capability to meet diverse architectural needs.
Enhanced Durability: The groin vault’s ability to handle increased loads more effectively than simple flat ceilings or barrel vaults contributed to the longevity and resilience of Roman architecture, which still stands as a testament to their engineering prowess.
Aesthetic Appeal: Beyond their structural benefits, groin vaults also added an aesthetic dimension to buildings. Their pleasing symmetrical form was used to enhance the interior spaces of structures, contributing to the grandeur and majestic appearance that is characteristic of Roman architecture.
Historical Significance: Understanding the fundamental design and applications of groin vaults offers insights into Roman architectural innovation and the evolution of building techniques. It also helps appreciate how these ancient solutions paved the way for future architectural developments, including the elaborate designs of medieval cathedrals.
These takeaways underscore the groin vault's importance not only as a structural element but also as a significant contributor to architectural design and history.
Architectural Features and Design
The Anatomy of the Groin Vault
Explore the structural and aesthetic features of groin vaults, and how they have been adapted in various architectural styles.
Subsections:
- Design Principles: Load distribution, light enhancement, and space utilization.
- Aesthetic Contributions: Impact on the visual grandeur of spaces.
- Case Studies: Examples from notable cathedrals and modern buildings.
Design Principles of Groin Vaults: Load Distribution, Light Enhancement, and Space Utilization
Load Distribution
Groin vaults are an architectural breakthrough primarily because of their ability to distribute loads effectively. By intersecting two barrel vaults at right angles, the resulting groin vault directs the weight of the structure down to the corners of the vault, rather than distributing it along the entire length of the wall. This allows for the use of thinner walls and the ability to support heavier loads, making buildings not only more stable but also capable of spanning larger spaces without the need for additional support.
Light Enhancement
One of the aesthetic and functional advantages of groin vaults is their ability to enhance interior lighting. The architectural design of groin vaults, especially in their application in Gothic cathedrals, incorporates elevated ceilings and clerestory windows. These elements work together to allow more natural light to penetrate the interior, creating not only a visually stunning space but also one that uses natural resources efficiently.
Space Utilization
Groin vaults dramatically improve space utilization within a structure. The architectural design of these vaults creates an uninterrupted overhead space, free from columns or other supporting structures that would otherwise obstruct the floor area. This feature is particularly useful in large public spaces, such as churches, cathedrals, and halls, where open, unobstructed interior spaces are necessary for both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Together, these design principles of groin vaults—load distribution, light enhancement, and space utilization—not only revolutionized architectural design during their initial period of use but continue to influence modern architecture today. These principles allow architects to explore new creative possibilities while addressing practical considerations of stability, lighting, and efficient use of space.
Aesthetic Contributions: Impact of Groin Vaults on Visual Grandeur
Groin vaults significantly influence the aesthetic appeal of architectural spaces, adding a sense of grandeur and visual interest that enhances both the functionality and the beauty of the structures in which they are used.
Creating Dramatic Interiors
Groin vaults are renowned for their ability to create dramatic and imposing interiors. The architectural form of the vault, with its intersecting arches and symmetrical design, draws the eye upward and makes spaces feel larger and more open. This vertical lift and the expansive feel are particularly impactful in large buildings like cathedrals, where the sense of ascendance and light contributes to the spiritual experience.
Enhancing Architectural Harmony
The use of groin vaults contributes to a harmonious architectural rhythm within a space. The repetitive patterns formed by the vaults create a cohesive visual experience that unifies the interior design. This symmetry and pattern not only please the eye but also impart a structured, orderly feel to the space, making complex buildings feel more navigable and coherent.
Complementing Decorative Elements
Groin vaults provide an ideal framework for incorporating intricate decorative elements, which were particularly popular in Gothic architecture. The surfaces of the vaults serve as a canvas for artists and craftsmen to add paintings, carvings, and other ornamental designs, enhancing the cultural and historical value of the buildings. These decorative embellishments make each vaulted ceiling unique and are a testament to the artisan skills of the period.
Maximizing Light Play
The architectural design of groin vaults, with their multiple curving surfaces, plays with light in a way that flat or less complex ceilings cannot. The way light interacts with the curves and angles of the vaults can create dynamic shadows and highlights, adding depth and vibrancy to the space. This manipulation of light not only enhances the aesthetic quality of the interior but also changes the ambiance throughout the day, reflecting the natural movement of sunlight.
In summary, the aesthetic contributions of groin vaults to architectural spaces are profound, influencing not just the structural integrity but also the visual and emotional impact of the buildings. Their ability to transform spaces into spectacular showcases of art and architecture continues to inspire admiration and awe in historical and contemporary contexts alike.
Case Studies: Groin Vaults in Notable Cathedrals and Modern Buildings
Groin vaults have been a defining element in the architecture of many famous structures, from medieval cathedrals to contemporary buildings. These case studies highlight the adaptability and lasting influence of groin vaults across different architectural eras and styles.
Notable Cathedrals
Cathedral of Saint Mary of the See (Seville Cathedral)
Seville Cathedral in Spain, the largest Gothic cathedral in the world, utilizes groin vaults to support its expansive and intricate interior. The vaults here are particularly notable for their height and the dramatic sense of verticality they provide, enhancing the cathedral's grandeur and the spiritual atmosphere within.Canterbury Cathedral
Located in Canterbury, England, this cathedral showcases the evolution of architectural styles from Romanesque to Gothic. The groin vaults in the choir, rebuilt in the 12th century, are an early example of Gothic architecture’s use of this feature to achieve greater heights and a more luminous interior.
Modern Buildings
Denver International Airport
The Jeppesen Terminal at Denver International Airport is a modern structure that uses a tensioned fabric version of the groin vault, creating a series of peaks and valleys in its roofline. This contemporary adaptation not only supports the massive roof structure but also provides a visually striking silhouette against the Colorado sky.The British Museum - Great Court
The Queen Elizabeth II Great Court at The British Museum, redesigned in the early 2000s, features a modern reinterpretation of the groin vault in its glass and steel roof. The roof covers the entire court, transforming the space into Europe's largest covered public square, demonstrating how traditional elements can be reimagined in modern materials to spectacular effect.
These case studies demonstrate the versatility and enduring appeal of groin vaults, showing that they can be as relevant today as they were in the past. Whether in the soaring spaces of Gothic cathedrals or the innovative designs of modern architecture, groin vaults continue to be a key element in creating dynamic, functional, and visually compelling spaces.
Key Takeaways: Appreciation of groin vaults in enhancing structural integrity and aesthetic beauty.
Gothic Architecture and Groin Vaults
Exploring the Symbiosis Between Groin Vaults and Gothic Design
This module delves into the critical role that groin vaults played in the development of Gothic architecture, a style renowned for its dramatic verticality and light-filled spaces.
Subsections:
- Introduction to Gothic Architecture: Characteristics and defining features of Gothic style.
- The Role of Groin Vaults in Gothic Structures: How groin vaults facilitated the construction of iconic Gothic cathedrals.
- Structural Innovations: Analysis of the engineering behind groin vaults that supported taller, more complex structures.
- Iconic Examples: Detailed look at specific cathedrals that epitomize the integration of groin vaults into Gothic architecture, such as Chartres Cathedral and Milan Cathedral.
Introduction to Gothic Architecture: Characteristics and Defining Features
Gothic architecture emerged in the High Middle Ages and became one of the most influential styles in European building design. Characterized by its soaring heights, pointed arches, and intricate ornamentation, Gothic architecture transformed the landscape of medieval cities and left an indelible mark on architectural history. Here, we explore the key characteristics and defining features of this iconic style.
Pointed Arches
One of the most distinctive features of Gothic architecture is the widespread use of pointed arches. Unlike the rounded arches of Romanesque architecture, Gothic arches rise to a point at their apex. These pointed arches not only add verticality to the structures but also distribute weight more efficiently, allowing for taller and more spacious interiors.
Ribbed Vaults
Gothic cathedrals are renowned for their intricate ribbed vaults, which form the ceilings and roofs of these monumental structures. Ribbed vaults consist of a framework of intersecting ribs that support the weight of the roof and distribute it down to the columns or walls below. This innovative structural system allowed for larger open spaces and enabled the creation of soaring, light-filled interiors.
Flying Buttresses
Flying buttresses are another hallmark of Gothic architecture, designed to provide additional support to the walls and distribute the outward thrust of the vaulted ceilings. These graceful, arched structures extend from the exterior of the building, counterbalancing the lateral forces exerted by the vaults and allowing for the construction of expansive windows and walls of stained glass.
Vertical Emphasis
Gothic architecture is characterized by its emphasis on verticality, with buildings reaching towards the heavens in a symbolic gesture of aspiration and spiritual transcendence. This vertical orientation is achieved through the use of tall, slender columns, pointed arches, and soaring spires, creating an awe-inspiring sense of height and majesty.
Ornate Decoration
Gothic buildings are often adorned with elaborate decoration, including sculpted stone carvings, intricate tracery, and colorful stained glass windows. These decorative elements serve both aesthetic and symbolic purposes, enriching the visual experience of the architecture and conveying religious narratives and allegories to the faithful.
Light and Space
Light plays a central role in Gothic architecture, symbolizing divine illumination and spiritual enlightenment. Large windows with delicate tracery allow natural light to flood the interiors, creating a luminous and ethereal atmosphere that transcends earthly concerns and inspires reverence.
In summary, Gothic architecture is defined by its pointed arches, ribbed vaults, flying buttresses, vertical emphasis, ornate decoration, and emphasis on light and space. These characteristics combine to create buildings that are not only structurally innovative but also spiritually uplifting, serving as enduring symbols of human creativity and aspiration.
The Role of Groin Vaults in Gothic Structures: Facilitating Iconic Cathedral Construction
Gothic cathedrals stand as enduring symbols of architectural innovation and human ingenuity, with groin vaults playing a pivotal role in their construction. Here's how groin vaults facilitated the creation of these iconic structures:
Structural Efficiency
Groin vaults, with their intersecting barrel vaults, allowed for a more efficient distribution of weight compared to traditional barrel vaults or flat ceilings. By directing the weight downwards to the supporting columns or walls at the corners, groin vaults relieved lateral pressure on the walls, enabling the construction of taller and more expansive buildings.
Height and Light
The use of groin vaults in Gothic cathedrals enabled architects to achieve unprecedented heights and create soaring interior spaces. These lofty ceilings, supported by the ribbed structure of the vaults, allowed for the incorporation of clerestory windows high above the ground level. The abundant natural light that flooded through these windows illuminated the interiors, creating a luminous and uplifting atmosphere that inspired awe and reverence.
Spacious Interiors
Groin vaults also contributed to the creation of spacious and open interiors within Gothic cathedrals. The intersection of the vaults at right angles allowed for the elimination of obstructive support columns or walls, creating uninterrupted expanses of floor space. This architectural feature facilitated the construction of large nave areas and transepts, accommodating congregations of worshippers and providing ample room for elaborate religious ceremonies and processions.
Architectural Unity
In addition to their structural benefits, groin vaults played a crucial role in achieving architectural unity and coherence within Gothic cathedrals. The repetitive rhythm of the intersecting vaults created a harmonious visual pattern that extended throughout the entire building. This sense of unity not only enhanced the aesthetic appeal of the architecture but also contributed to the overall stability and integrity of the structure.
Support for Elaborate Roof Systems
Groin vaults provided a robust framework for supporting the elaborate roof systems of Gothic cathedrals, including the timber frameworks, lead roofing, and decorative elements such as pinnacles and spires. The inherent strength and stability of groin vaults allowed for the construction of complex roof structures that could withstand the test of time and the elements.
In summary, groin vaults were instrumental in the construction of iconic Gothic cathedrals, facilitating their towering heights, expansive interiors, and intricate architectural details. By providing structural efficiency, supporting lofty ceilings, creating spacious interiors, achieving architectural unity, and supporting elaborate roof systems, groin vaults helped transform architectural vision into reality, leaving a lasting legacy of awe-inspiring beauty and engineering prowess.
Structural Innovations: Engineering Analysis of Groin Vaults in Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture stands as a testament to the ingenuity of medieval engineers, and groin vaults played a crucial role in supporting taller and more complex structures. Here's an analysis of the engineering principles behind groin vaults:
Load Distribution
One of the key engineering innovations of groin vaults is their ability to distribute weight more effectively than traditional barrel vaults. By intersecting two barrel vaults at right angles, groin vaults transfer the downward force of the roof to the supporting columns or walls at the corners. This distribution of weight minimizes lateral thrust and allows for the construction of taller and more expansive buildings without the need for thick, heavy walls.
Structural Stability
Groin vaults enhance structural stability by providing multiple points of support along their length. The intersecting ribs of the vaults create a network of arches that work together to resist the forces of compression and tension. This structural redundancy strengthens the vault system and helps prevent collapse, even in the event of uneven settling or seismic activity.
Buttressing Systems
To further enhance the stability of groin vaults, Gothic architects developed sophisticated buttressing systems, including flying buttresses and piers. Flying buttresses are arched structures that extend from the exterior of the building to support the outward thrust of the vaults, while piers provide additional vertical support. Together, these elements form a robust framework that counteracts the lateral forces exerted by the vaulted ceilings, allowing for the construction of expansive windows and walls of stained glass.
Material Innovation
The use of innovative materials, such as limestone and mortar, contributed to the success of groin vaults in Gothic architecture. Limestone, prized for its strength and durability, was quarried locally and carved into precisely shaped blocks to form the ribs and keystones of the vaults. Mortar, made from a mixture of lime, sand, and water, provided a strong adhesive bond between the stones, ensuring structural integrity and stability.
Geometric Precision
Achieving the complex geometric shapes of groin vaults required meticulous planning and execution. Gothic architects employed advanced techniques of geometry and mathematics to calculate the exact angles and dimensions of the vaults, ensuring a precise fit and optimal load distribution. Skilled craftsmen then carved and assembled the individual stones with painstaking accuracy, creating vaults that were both structurally sound and visually striking.
In summary, the engineering behind groin vaults in Gothic architecture represents a remarkable achievement in structural innovation. Through careful design, meticulous craftsmanship, and the use of innovative materials and techniques, medieval engineers were able to create vaulted ceilings that supported taller, more complex structures while embodying the beauty and grandeur of the Gothic style.
Iconic Examples: Integration of Groin Vaults in Gothic Cathedrals
Gothic cathedrals are renowned for their breathtaking beauty and innovative use of architectural elements, including groin vaults. Two prime examples of Gothic cathedrals that epitomize the integration of groin vaults are Chartres Cathedral in France and Milan Cathedral in Italy. Let's take a detailed look at each:
Chartres Cathedral, France
Chartres Cathedral, located in the picturesque town of Chartres, France, is a masterpiece of Gothic architecture and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Built in the 12th and 13th centuries, Chartres Cathedral showcases the evolution of Gothic design, including the innovative use of groin vaults.
Groin Vaults in Chartres Cathedral:
Nave and Choir: The nave and choir of Chartres Cathedral feature soaring groin vaults that create a sense of height and grandeur. These vaults support the massive stone roof and distribute the weight evenly to the columns and walls below, allowing for the construction of expansive, light-filled interiors.
Stained Glass Windows: One of the most remarkable features of Chartres Cathedral is its collection of stained glass windows, which adorn the clerestory above the groin vaults. These windows, with their intricate tracery and vibrant colors, illuminate the interior with a celestial glow, creating a transcendent atmosphere that has captivated visitors for centuries.
Flying Buttresses: Chartres Cathedral is supported by a system of flying buttresses, which extend from the exterior walls to counteract the outward thrust of the groin vaults. These buttresses, adorned with delicate carvings and sculptures, add to the cathedral's structural stability while enhancing its visual beauty.
Milan Cathedral, Italy
Milan Cathedral, or Duomo di Milano, is one of the largest and most magnificent Gothic cathedrals in the world. Built over six centuries, from the 14th to the 19th century, Milan Cathedral showcases the enduring legacy of Gothic architecture and the innovative use of groin vaults.
Groin Vaults in Milan Cathedral:
Interior Spaces: The interior of Milan Cathedral is characterized by its vast expanses of groin vaults, which create a sense of awe-inspiring spaciousness. These vaults support the massive stone roof and allow for the inclusion of towering columns and intricate sculptural details, such as the famous forest of stone pinnacles that rise from the floor to the ceiling.
High Altar Area: The high altar area of Milan Cathedral features a series of intersecting groin vaults that form a majestic canopy over the sanctuary. This intricate vaulting system, adorned with ornate carvings and decorative motifs, serves as a focal point for religious ceremonies and rituals, symbolizing the spiritual aspirations of the faithful.
Exterior Façade: The exterior façade of Milan Cathedral is adorned with a profusion of spires, statues, and decorative elements, all supported by a network of groin vaults and flying buttresses. These architectural features contribute to the cathedral's striking silhouette and serve as a testament to the skill and craftsmanship of the artisans who built it.
In summary, Chartres Cathedral and Milan Cathedral exemplify the integration of groin vaults into Gothic architecture, showcasing the structural innovation, aesthetic beauty, and spiritual significance of these iconic architectural elements. From their soaring interiors to their elaborately adorned exteriors, these cathedrals continue to inspire wonder and admiration, inviting visitors to marvel at the enduring legacy of Gothic design.
Architects and Innovation with Groin Vaults in Gothic Cathedrals
- Stories of the architects behind famous Gothic cathedrals and how they innovatively used groin vaults to solve structural challenges and achieve higher ceilings and larger windows.
Groin vaults have been central to the evolution of architectural design, particularly in Gothic cathedrals, where they were used not just for their structural benefits but also for their aesthetic impact. The architects behind these grand edifices often pushed the boundaries of existing technology, using groin vaults to address and overcome significant architectural challenges. Here are some stories of these innovative architects and their iconic works:
Villard de Honnecourt – The Innovator of Early Gothic Architecture
Villard de Honnecourt, a 13th-century architect, is known for his sketchbook that provides valuable insights into Gothic architecture. Although not directly credited with building a specific cathedral, his drawings include detailed plans for using groin vaults to enhance structural integrity and verticality in cathedral designs. His work influenced the use of groin vaults in creating higher ceilings and larger windows, which became hallmarks of Gothic architecture.
Peter Parler – Transforming Prague Cathedral
Peter Parler was one of the most influential Gothic architects of the 14th century, known especially for his work on St. Vitus Cathedral in Prague. Parler's innovative use of groin vaults allowed for the integration of larger windows into the cathedral's clerestory, flooding the interior with natural light and emphasizing verticality. His approach to vaulting also enabled the complex web of supports necessary for the cathedral's soaring arches, showcasing his mastery of both form and function.
Jean de Chelles and Pierre de Montreuil – Pioneers at Notre Dame de Paris
Jean de Chelles and Pierre de Montreuil played pivotal roles in the development of Notre Dame Cathedral in Paris. Jean de Chelles initiated the use of groin vaults in the transept and choir to support higher ceilings and larger windows, significantly influencing the cathedral’s iconic design. Pierre de Montreuil later contributed to the refinement of these techniques, enhancing the structural stability of the vaults and enabling even more ambitious uses of glass and light.
The Unnamed Masters of Chartres Cathedral
Chartres Cathedral, one of the finest examples of French Gothic architecture, showcases the genius of unnamed medieval architects who utilized groin vaults to solve structural problems caused by earlier designs. The cathedral's nave, rebuilt after a fire, features complex groin vaults that support the roof while allowing for a stunning array of stained glass windows. This architectural solution was not only innovative for its time but also set a standard for future Gothic cathedrals.
These stories of Gothic architects and their creative use of groin vaults underscore the deep connection between architectural innovation and aesthetic vision. Through their work, these architects managed to turn structural elements into opportunities for beautification, forever changing the landscape of European architecture. Their legacy demonstrates how technical challenges can lead to breakthroughs that resonate through the ages, influencing both the practical and the profound aspects of building design.
This module will not only enrich the learner’s understanding of Gothic architecture but also illustrate the timeless influence of groin vaults in shaping architectural history and practice. By examining the integration of groin vaults into Gothic buildings, learners can appreciate the architectural achievements and the seamless blend of form and function that these structures represent.
Key Takeaways: The Evolution of Gothic Architecture with Groin Vaults
Structural Innovation: Groin vaults played a pivotal role in the evolution of Gothic architecture by allowing architects to achieve unprecedented heights and expansive interior spaces. Their structural efficiency enabled the construction of soaring cathedrals and palaces, showcasing the engineering prowess of the era.
Spatial Transformation: The introduction of groin vaults revolutionized the spatial experience of Gothic buildings, creating vast, open interiors flooded with natural light. These spaces served not only as places of worship but also as expressions of divine grandeur and human aspiration.
Aesthetic Splendor: Groin vaults contributed to the aesthetic splendor of Gothic architecture, adding verticality, rhythm, and drama to building facades and interiors. Their intersecting forms created intricate patterns of light and shadow, enhancing the spiritual atmosphere and awe-inspiring beauty of religious and secular structures alike.
Cultural Significance: The widespread adoption of groin vaults in Gothic architecture reflects the cultural and religious values of medieval society. These architectural marvels served as symbols of faith, power, and prosperity, embodying the aspirations and beliefs of the communities that built them.
Legacy and Influence: The legacy of groin vaults in Gothic architecture endures to this day, inspiring architects and designers to explore new possibilities in spatial design and structural expression. Their timeless appeal continues to shape contemporary architecture, serving as a testament to the enduring legacy of Gothic innovation.
In summary, groin vaults were instrumental in the evolution of Gothic architecture, transforming both the functionality and aesthetics of religious and secular buildings. Their structural ingenuity, spatial transformation, aesthetic splendor, cultural significance, and lasting influence make groin vaults a defining feature of Gothic architectural heritage.
Modern Applications and Innovations
Groin Vaults in Contemporary Architecture
Discuss the adaptation and influence of groin vaults in modern architectural practices, including sustainable and innovative designs.
Subsections:
- Modern Adaptations: Use in contemporary architecture.
- Innovative Materials and Techniques: New materials enhancing traditional designs.
- Sustainability: Role in eco-friendly building practices.
Groin Vaults in Contemporary Architecture: Adaptation and Influence
While groin vaults are often associated with medieval Gothic cathedrals, their influence extends far beyond the Middle Ages. In contemporary architecture, architects continue to draw inspiration from groin vaults, adapting their form and function to suit modern design principles and sustainability practices. Here's a discussion on the adaptation and influence of groin vaults in modern architectural practices:
Structural Innovation
In contemporary architecture, groin vaults are often employed as a structural solution to support large spans and create open, airy spaces. By utilizing modern materials and engineering techniques, architects can design groin vaults that span vast distances without the need for internal supports, allowing for greater flexibility in space planning and layout.
Aesthetic Continuity
While contemporary architecture embraces new forms and materials, many architects seek to maintain a sense of continuity with architectural traditions of the past. Groin vaults offer a way to achieve this by providing a link to historical building techniques and aesthetics. By incorporating groin vaults into modern designs, architects can evoke a sense of timelessness and heritage while creating spaces that are functional and visually compelling.
Sustainable Design
Groin vaults can also contribute to sustainable design practices by optimizing natural ventilation and daylighting. The open, expansive interiors created by groin vaults allow for improved airflow and circulation, reducing the need for mechanical ventilation systems and minimizing energy consumption. Additionally, the use of large windows and skylights in conjunction with groin vaults can maximize natural light penetration, reducing the reliance on artificial lighting and lowering carbon emissions.
Innovative Applications
Innovative architects are pushing the boundaries of groin vault design, exploring new materials, forms, and construction techniques. For example, some contemporary groin vaults incorporate lightweight materials such as carbon fiber or composite polymers, allowing for greater design freedom and structural efficiency. Others experiment with parametric design and digital fabrication technologies to create bespoke groin vaults with intricate geometries and patterns.
Cultural Revival
In regions with rich architectural heritage, contemporary architects are reviving the use of groin vaults as a way to reconnect with local traditions and craftsmanship. By incorporating groin vaults into modern buildings, architects pay homage to the architectural legacy of their ancestors while creating spaces that are relevant to contemporary needs and lifestyles.
In conclusion, groin vaults continue to inspire and influence contemporary architecture, serving as a versatile structural element that bridges the gap between past and present. From their role in sustainable design practices to their aesthetic appeal and cultural significance, groin vaults remain a timeless symbol of architectural innovation and creativity in the modern built environment.
Modern Adaptations: Groin Vaults in Contemporary Architecture
Contemporary architects are reimagining the traditional groin vault and incorporating it into innovative designs that reflect modern sensibilities and address current architectural challenges. Here's how groin vaults are being used in contemporary architecture:
Structural Versatility
Groin vaults are celebrated for their ability to span large distances without the need for internal supports, making them ideal for creating expansive interior spaces in contemporary buildings. Architects leverage this structural versatility to design open-plan layouts that promote flexibility and connectivity, catering to the evolving needs of modern occupants.
Architectural Expression
In contemporary architecture, groin vaults are not merely structural elements but also architectural features that contribute to the overall aesthetic of a building. Architects experiment with different forms, materials, and textures to create groin vaults that serve as focal points, adding visual interest and character to the built environment.
Sustainable Design
The sustainable design movement has spurred interest in groin vaults as they offer opportunities to optimize natural ventilation and daylighting. Architects strategically position openings within the vaults to harness prevailing winds and maximize the ingress of natural light, reducing energy consumption and enhancing occupant comfort in contemporary buildings.
Adaptive Reuse
Groin vaults are increasingly being repurposed in adaptive reuse projects, where historic structures are transformed into modern spaces for new purposes. Architects preserve and celebrate the existing groin vaults while integrating contemporary interventions to meet the functional requirements of the reimagined building, creating a harmonious juxtaposition of old and new.
Iconic Landmarks
Contemporary architects use groin vaults to create iconic landmarks that define the skyline of cities around the world. From cultural centers and museums to commercial complexes and transportation hubs, these architectural marvels showcase the enduring appeal and adaptability of groin vaults in contemporary urban contexts.
Technological Integration
Advancements in technology, such as parametric design software and digital fabrication techniques, enable architects to push the boundaries of groin vault design. Complex geometries and intricate patterns can be precisely engineered and fabricated, allowing for the creation of bespoke groin vaults that embody the spirit of innovation and experimentation in contemporary architecture.
In summary, groin vaults continue to play a significant role in contemporary architecture, offering structural versatility, architectural expression, and opportunities for sustainable design. Whether as part of adaptive reuse projects or in the creation of iconic landmarks, groin vaults serve as timeless elements that bridge the past with the present and inspire the architecture of the future.
Innovative Materials and Techniques: Enhancing Traditional Designs
In contemporary architecture, the integration of innovative materials and construction techniques has revolutionized the way traditional architectural elements like groin vaults are conceived and realized. Here's a look at how new materials are enhancing traditional designs:
Lightweight Composites
Architects are exploring the use of lightweight composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, to construct groin vaults with greater efficiency and versatility. These materials offer high strength-to-weight ratios, allowing for the creation of slender, yet robust vaults that minimize material usage and construction time.
Engineered Timber
Advancements in engineered timber technologies, such as cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glue-laminated timber (glulam), are enabling the construction of groin vaults with sustainable and renewable materials. Engineered timber offers the strength and durability required for structural applications while providing architects with greater design flexibility and aesthetic possibilities.
3D Printing
The emergence of 3D printing technology has opened up new possibilities for creating complex and customized groin vaults with unprecedented precision and efficiency. Architects can use 3D printing to fabricate intricate formwork and molds for casting concrete or other materials, enabling the production of bespoke vaults that push the boundaries of traditional craftsmanship.
Recycled and Reclaimed Materials
Sustainability concerns have led architects to explore the use of recycled and reclaimed materials in groin vault construction. Salvaged stone, reclaimed timber, and recycled metal elements can add character and authenticity to contemporary designs while reducing the environmental impact of construction projects.
Transparent and Translucent Materials
Innovative transparent and translucent materials, such as glass and polycarbonate panels, are being incorporated into groin vault designs to introduce new possibilities for natural lighting and visual transparency. These materials allow for the creation of light-filled interiors that blur the boundaries between indoor and outdoor spaces, while maintaining structural integrity and thermal performance.
Smart Materials
The development of smart materials, including shape-memory alloys, self-healing polymers, and responsive membranes, holds promise for enhancing the performance and functionality of groin vaults in contemporary architecture. These materials can adapt to changing environmental conditions, improve energy efficiency, and enhance occupant comfort, ushering in a new era of dynamic and responsive building design.
In summary, the integration of innovative materials and techniques is transforming the traditional groin vault into a versatile and sustainable architectural element. By embracing new materials and construction methods, architects are pushing the boundaries of design possibilities and creating groin vaults that are not only structurally sound but also aesthetically compelling and environmentally responsible.
Sustainability: The Role of Groin Vaults in Eco-Friendly Building Practices
In the realm of eco-friendly building practices, groin vaults offer several advantages that contribute to sustainable architecture. Here's how groin vaults play a crucial role in promoting sustainability:
Natural Ventilation and Daylighting
Groin vaults are conducive to natural ventilation and daylighting, allowing architects to design buildings that minimize reliance on mechanical heating, cooling, and lighting systems. The open, expansive interiors created by groin vaults facilitate airflow and light penetration, reducing energy consumption and enhancing occupant comfort.
Thermal Mass Benefits
The use of dense materials like stone or concrete in groin vault construction provides thermal mass benefits, helping to regulate indoor temperatures and reduce heating and cooling loads. Groin vaults can absorb heat during the day and release it slowly at night, resulting in more stable and energy-efficient building environments.
Sustainable Materials and Construction Techniques
Groin vaults can be constructed using sustainable materials such as locally sourced stone, recycled concrete, or engineered timber, reducing the environmental impact of building projects. Additionally, innovative construction techniques, such as prefabrication and modular assembly, can further enhance the sustainability of groin vault construction by minimizing waste and resource consumption.
Longevity and Durability
Groin vaults are inherently durable and long-lasting, with many historical examples standing strong for centuries. By incorporating groin vaults into contemporary buildings, architects can create structures that are built to last, reducing the need for frequent maintenance, repair, and replacement over time.
Adaptive Reuse and Historic Preservation
In adaptive reuse projects, groin vaults in existing buildings can be retained and repurposed, preserving valuable architectural heritage and reducing the environmental impact of new construction. By breathing new life into old structures, architects can minimize waste and embodied energy while honoring the cultural significance of historical buildings.
Integration with Green Technologies
Groin vaults can be seamlessly integrated with green technologies such as photovoltaic panels, rainwater harvesting systems, and green roofs, further enhancing the sustainability of buildings. These technologies can be incorporated into the design of groin vaulted structures to optimize energy efficiency, water conservation, and overall environmental performance.
In summary, groin vaults play a significant role in eco-friendly building practices by promoting natural ventilation and daylighting, leveraging thermal mass benefits, utilizing sustainable materials and construction techniques, ensuring longevity and durability, enabling adaptive reuse and historic preservation, and integrating with green technologies. As architects continue to prioritize sustainability in their designs, groin vaults offer a versatile and environmentally responsible solution for creating buildings that are both functional and environmentally friendly.
Key Takeaways: Ancient Techniques Reinvented in Modern Architecture
Historical Continuity: Groin vaults, originating from ancient Roman engineering, continue to inspire modern architects with their structural elegance and aesthetic appeal. The reinvention of these ancient techniques in contemporary architecture serves as a testament to their enduring relevance and adaptability.
Structural Innovation: In modern architecture, groin vaults are not merely relics of the past but dynamic elements that contribute to innovative structural solutions. Architects leverage advanced materials, construction techniques, and digital technologies to reimagine groin vaults in ways that meet the demands of today's built environment.
Aesthetic Evolution: While rooted in tradition, modern groin vaults embrace new forms, materials, and design principles to create spaces that are both functional and visually captivating. The reinvention of groin vaults in contemporary architecture reflects an ongoing dialogue between past and present, tradition and innovation.
Sustainable Practices: Groin vaults play a role in sustainable architecture by facilitating natural ventilation, daylighting, and thermal mass benefits. Architects integrate groin vaults with green technologies and sustainable materials to create buildings that minimize environmental impact while honoring architectural heritage.
Cultural Heritage: The reinvention of ancient techniques like groin vaults allows architects to preserve and celebrate cultural heritage while addressing contemporary needs. Through adaptive reuse and historic preservation, groin vaults serve as a link between past and present, connecting us to our architectural roots.
Technological Integration: Groin vaults in modern architecture benefit from advancements in technology, such as 3D printing, parametric design, and digital fabrication. These tools enable architects to push the boundaries of groin vault design, creating structures that are both structurally sound and visually stunning.
The reinvention of ancient techniques like groin vaults in modern architecture underscores the timeless appeal and adaptability of these architectural elements. By embracing tradition while embracing innovation, architects ensure that groin vaults remain a cornerstone of architectural excellence in the 21st century and beyond.
Questions and Answers - FAQs
Addressing Common Queries
This section will clarify frequent questions, aiding in a deeper understanding of the groin vault's significance and utility.
FAQs: Groin Vaults in Architecture
1. What makes groin vaults uniquely effective in architecture?
Groin vaults offer a combination of structural efficiency and aesthetic versatility that make them indispensable in architecture. Structurally, groin vaults distribute weight evenly, allowing for large interior spaces without the need for supporting columns. Aesthetically, groin vaults provide opportunities for intricate detailing, dramatic lighting effects, and timeless elegance, enhancing the visual appeal of buildings.
2. Can groin vaults be adapted for use in non-traditional buildings?
Yes, groin vaults can be adapted for use in a wide range of non-traditional buildings, including contemporary homes, commercial structures, and cultural centers. Examples include modern residences with open-plan layouts, innovative office spaces with dramatic ceiling heights, and art galleries with dynamic exhibition spaces. Groin vaults bring a sense of architectural heritage and spatial drama to these unconventional settings.
3. How do groin vaults contribute to sustainable architecture?
Groin vaults contribute to sustainable architecture in several ways. Firstly, their structural efficiency minimizes the need for internal supports, maximizing interior space and reducing material usage. Secondly, groin vaults can be constructed using sustainable materials such as timber, recycled concrete, or locally sourced stone, reducing environmental impact. Additionally, the open, light-filled interiors created by groin vaults promote natural ventilation and daylighting, reducing energy consumption and enhancing occupant comfort.
4. What are some challenges in constructing groin vaults today?
Constructing groin vaults today presents challenges related to technical complexity, material selection, and construction logistics. Achieving precise curvature and symmetry in groin vaults requires skilled craftsmanship and advanced construction techniques. Additionally, selecting appropriate materials that balance structural integrity, durability, and sustainability can be challenging. Finally, coordinating the assembly of groin vaults on-site, especially in large-scale projects, requires meticulous planning and coordination among architects, engineers, and construction teams.
Groin Vaults in Depth: A Free Comprehensive Course on Architectural Mastery
Conclusion: Reflecting on Our Architectural Course
As we bring our exploration of the groin vault to a close, it's essential to reflect on the key takeaways and consider the implications of this architectural form in modern design.
Structural Elegance and Efficiency: Throughout history, groin vaults have demonstrated their structural elegance and efficiency, providing support for expansive spaces without the need for cumbersome internal supports. Understanding the fundamental mechanics of groin vaults opens up a world of possibilities for creating open, light-filled interiors that inspire and delight.
Aesthetic Versatility: Beyond their structural prowess, groin vaults offer aesthetic versatility, allowing architects to play with light, shadow, and form to create visually captivating spaces. Whether in the soaring heights of a Gothic cathedral or the minimalist lines of a contemporary residence, groin vaults add a sense of drama and grandeur to architectural compositions.
Connection to Tradition and Innovation: The reinvention of ancient techniques like groin vaults in contemporary architecture highlights the enduring appeal and adaptability of these architectural elements. By embracing tradition while embracing innovation, architects ensure that groin vaults remain relevant in the ever-evolving landscape of modern design.
Sustainability and Sensibility: Groin vaults contribute to sustainable architecture by promoting natural ventilation, daylighting, and thermal efficiency. By integrating groin vaults with green technologies and sustainable materials, architects can create buildings that are not only structurally sound but also environmentally responsible.
Challenges and Opportunities: While constructing groin vaults presents technical and material challenges, it also offers opportunities for creative problem-solving and collaboration. By overcoming these challenges, architects can push the boundaries of groin vault design and create spaces that inspire awe and admiration.
In conclusion, the groin vault is more than just a structural element; it's a symbol of architectural ingenuity, creativity, and innovation. By understanding its history, embracing its possibilities, and pushing its boundaries, we can continue to unlock the full potential of this timeless architectural form in the world of modern design.
Further Exploration
Related Books:
"The Gothic Enterprise: A Guide to Understanding the Medieval Cathedral" by Robert A. Scott: Get into the intricate world of Gothic architecture and explore the fascinating history behind the construction of medieval cathedrals.
"Structural Engineering for Architects: A Handbook" by Peter Evans: Gain insights into the structural principles and engineering techniques that underpin iconic architectural forms like the groin vault.
"Modern Architecture: A Critical History" by Kenneth Frampton: Explore the evolution of modern architecture and its impact on contemporary design practices, including the reinterpretation of traditional architectural elements.
Courses:
Coursera: "Understanding Architecture": This course offers a comprehensive overview of architectural history, theory, and practice, providing learners with a solid foundation for further exploration.
edX: "Sustainable Architecture: Design and Construction": Dive into the principles of sustainable architecture and learn how to integrate environmental considerations into the design and construction of buildings, including the use of groin vaults.
Udemy: "Introduction to Parametric Design in Architecture": Explore the possibilities of parametric design tools in architectural practice and discover how they can be used to create innovative groin vault structures and other architectural forms.
