Contemporary Homes & Modern Windows in 2024: Expansive Glass

Course Outline: Expansive Windows in Contemporary Architecture
Introduction to Expansive Windows in Modern Design: Tips on how to incorporate high windows to create a stylish home
This is a comprehensive course on Expansive Windows in Contemporary Architecture. This free course is designed to take you through the fascinating world of modern architectural design, with a special focus on expansive glass windows. We aim to explore their history, design, and the unique way they transform spaces from ordinary to extraordinary. By the end of this course, you'll understand not just the aesthetics but the functionality, engineering, and environmental considerations behind these architectural marvels.
Contemporary Design Features: Expansive Windows & Glass
Section 1: The History & Evolution of Expansive Windows
History of Architectural Glass
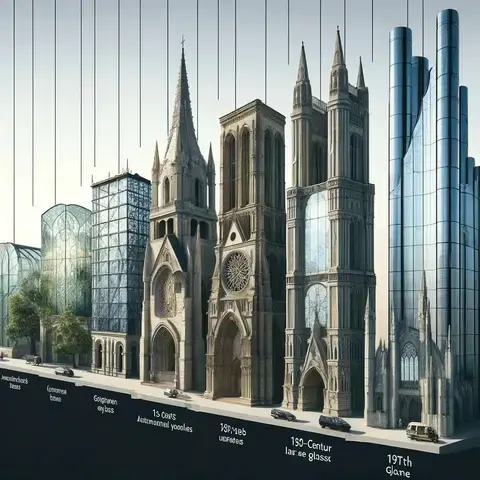

- Content: We start with the origins of glass in architecture, tracing its development from small, primitive panes to the large, structural components we see today. This section will highlight key milestones and technological advancements that have allowed architects to increasingly use glass as a dominant material.
Milestones in Expansive Window Design: Examples
- Iconic buildings through history that marked a significant use of expansive windows.
- Content: Discuss specific buildings and architects that have played pivotal roles in integrating expansive windows into their designs, showcasing how these elements have become synonymous with modern architecture.
Section 2: Design and Aesthetics of Expansive Windows

Characteristics of Modern Windows
- Close-up look of modern expansive windows highlighting their unique characteristics.
- Content: Explore the technical and aesthetic features of modern expansive windows, including frame materials, glass technology (like thermal and UV coatings), and the interplay of light and space they facilitate.
Contemporary Homes with Expansive Windows

- Content: Provide examples of contemporary homes where expansive windows play a crucial role in design. Discuss how these windows influence the living experience, connect indoor and outdoor spaces, and contribute to the home's energy efficiency.
The Impact on Interior Spaces: Neutral Living Rooms
- Image concept: A neutral-toned contemporary living room flooded with natural light from expansive windows.
- Content: Focus on the interior design aspect, particularly how expansive windows can transform living spaces. Emphasize the use of neutral palettes to enhance the spaciousness and light.
Section 3: Technical Aspects and Innovations
Engineering Behind Expansive Windows

- Content: Dive into the structural engineering that makes large windows possible, including safety considerations, load-bearing aspects, and innovative materials that enhance durability and insulation.
Sustainable Design and Energy Efficiency
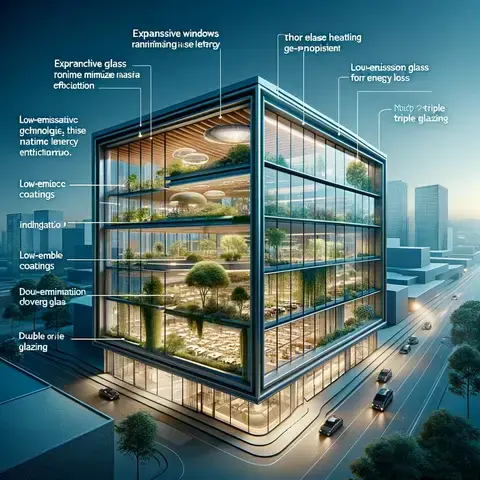
- Content: Discuss the role of expansive windows in sustainable design, focusing on energy efficiency, passive solar heating, and ventilation. Highlight advancements in glass technology that minimize energy loss.
Section 4: Future Trends and Innovations
The Future of Expansive Windows in Architecture

- Content: Speculate on the future developments in expansive window technology and design. Cover potential innovations in materials and construction techniques that could further transform architecture.
Conclusion: The Art and Science of Expansive Windows
Wrap up the course by emphasizing the balance between the art of design and the science of engineering that expansive windows represent. Highlight how they exemplify the evolving relationship between humans and their built environment, offering both challenges and opportunities for the future of architecture.
Section 5: Designing and Installing Expansive Windows: Guidelines and Tips

5.1 Understanding the Fundamentals of Expansive Window Installation
- Content: This section will provide a foundational understanding of the entire process involved in designing and installing expansive windows. Key considerations such as structural support, window orientation, and integration with the building's architecture will be covered.
5.2 Selecting the Right Materials and Glass Technology
- Image concept: Diagrams comparing different frame materials and glass types used in expansive windows, highlighting their pros and cons.
- Content: Discuss the importance of selecting the appropriate materials for frames (like aluminum, wood, or vinyl) and glass (such as double-glazed, low-E, or tinted) to meet specific aesthetic, thermal, and structural requirements.
5.3 Design Tips for Integrating Expansive Windows
- Image concept: A series of modern homes showcasing various design strategies for incorporating large windows, emphasizing aspects like natural light, views, and aesthetic coherence.
- Content: Offer practical design tips for architects and homeowners looking to integrate expansive windows into their projects. Topics include maximizing natural light, enhancing views, ensuring privacy, and maintaining energy efficiency.
5.4 Technical Considerations for Installation
- Image concept: Technical drawings highlighting key installation details of expansive windows, focusing on waterproofing, load distribution, and thermal bridging.
- Content: Delve into the technical aspects critical to the successful installation of expansive windows, including load distribution, waterproofing, insulation, and addressing thermal bridging to prevent heat loss.
5.5 Maintaining Aesthetic Balance and Functionality
- Image concept: Interiors showing the balance between aesthetic appeal and functionality achieved through the strategic placement and sizing of expansive windows.
- Content: Explore how to maintain an aesthetic balance and functionality with expansive windows, considering factors like the scale of the windows relative to the space, the interplay between interior and exterior, and the functional aspects like ventilation and sun control.
Questions and Answers FAQs
FAQ section, designed to answer your most pressing questions about windows in a clear, straightforward manner. This resource is tailored for those looking to learn more about different types of windows, their definitions, and specific characteristics. Whether you're a student, professional, or just curious, you'll find concise answers that get straight to the point.
Window Types and Definitions
What are expansive windows?
Expansive windows are large windows that cover a significant portion of a wall. They are designed to let in a lot of light and offer wide views of the outside. These windows can make a room feel more open and connected to the outdoor environment.
What are giant windows called?
Giant windows are often referred to as "expansive windows" or "floor-to-ceiling windows." These terms describe windows that are very large, often spanning from the floor to the ceiling, providing an unobstructed view and maximum natural light.
What are full height windows called?
Full height windows are typically called "floor-to-ceiling windows." As the name suggests, they extend from the floor to the ceiling, offering extensive views and filling the room with natural light.
What is a high window in a room called?
A high window in a room is commonly known as a "transom window." These are usually narrow windows placed above a door or another window, adding more light and sometimes ventilation to a room without compromising privacy.
What is a highlight window?
A highlight window is another term for a transom window. It's placed high up on the wall, often near the ceiling, to let in light while maintaining privacy and wall space for furniture or other design elements.
What are special shape windows?
Special shape windows refer to windows that don't have standard rectangular or square shapes. They can be circular, triangular, hexagonal, or any other non-standard shape, often used as architectural accents.
What are curved windows called?
Curved windows are often referred to as "arched windows" or "bow windows." Arched windows have a curved top, while bow windows form a gentle outward curve across the wall, creating a rounded appearance from the outside.
What is a Palladian window called?
A Palladian window is a large window that is divided into three parts, with a larger, arched window in the center and two smaller, flat-topped windows on each side. This design is named after the Italian architect Andrea Palladio, who popularized this style in the Renaissance.
What are French windows?
French windows are large windows that also serve as doors. They usually open from the center and are fitted with glass panes throughout their length, offering extensive views and access to a balcony, garden, or patio.
What are French windows called?
French windows are often simply called "French doors" in many contexts. While technically doors, they function as large windows, providing both access and ample natural light, similar to a door-window hybrid.
Window Installation
Installing new windows in your home is a critical process that can greatly affect your home's appearance, energy efficiency, and comfort. This section of FAQs covers everything from the basics of window installation to specific queries about measurement and legal considerations. Our goal is to provide clear, straightforward answers for those looking to understand more about the window installation process.
How do you install new windows in a house?
Installing new windows involves several steps:
- Preparation: Before starting, ensure you have all necessary tools and materials. Measure the window opening accurately to ensure the new window will fit.
- Removal of the Old Window: Carefully remove the existing window, taking care not to damage the surrounding wall or opening.
- Prepping the Opening: Clean the opening and check for any damage. Repair if necessary to ensure a snug fit for the new window.
- Installing the New Window: Place the new window in the opening. Use shims to adjust for a level fit. Once positioned correctly, secure the window in place with screws.
- Sealing: Apply caulking around the outside of the window to seal it and prevent air and water leaks.
- Finishing Touches: Install any trim or molding as needed. Test the window to ensure it opens, closes, and locks properly.
How to legally install windows?
Legally installing windows requires following local building codes and regulations, which can vary by location. Typically, this involves:
- Obtaining a Permit: Many areas require a permit for window installation. Check with your local building department to understand the requirements.
- Following Building Codes: Ensure the installation meets all relevant building codes, which may specify types of windows, energy efficiency standards, and installation methods.
- Hiring Qualified Contractors: In some cases, the law may require that windows be installed by licensed professionals. Even if not legally required, hiring experienced installers can ensure the job is done correctly and safely.
Which is the best way to install windows?
The best way to install windows depends on the type of window, the construction of the house, and specific needs like energy efficiency and aesthetics. However, hiring a professional installer who can assess these factors and ensure the installation complies with local codes and manufacturer recommendations is generally advisable.
What is window installation?
Window installation is the process of fitting a new window into a building's wall. It involves preparing the opening, securing the window in place, ensuring it is level and sealed against the elements, and finishing the installation for both function and appearance.
Are windows hard to install?
The difficulty of installing windows can vary widely depending on the type of window, the location, and the existing structure. Simple replacements in a standard size might be manageable for a DIY enthusiast with the right tools and knowledge. However, large, heavy, or complex installations, especially in new constructions or requiring structural modifications, are typically best left to professionals.
Do you install windows from inside or outside?
Windows can be installed from either the inside or outside, depending on the specific situation and type of window. Many installers prefer working from the outside for easier access and the ability to properly seal the exterior against water and air leaks. However, interior installations are sometimes necessary or more practical, especially in multi-story buildings.
How do you measure a window?
To measure a window accurately:
- Width: Measure the width of the window at the top, middle, and bottom from the inside of the frame. Use the smallest measurement to ensure the new window will fit.
- Height: Measure the height on the left, middle, and right sides from the top of the sill to the underside of the top frame. Again, use the smallest measurement.
- Depth: Measure the depth of the window from the outside face of the exterior trim to the inside face of the interior trim (not including any obstructions like pulleys or parting strips). Always double-check your measurements to avoid errors.
Window Manufacturing
The process of creating windows is both an art and a science, requiring precision, careful material selection, and an understanding of architectural requirements. This section addresses common questions about window manufacturing, whether you're considering DIY options or simply curious about how windows are made.
Can you make your own windows?
Yes, it's possible to make your own windows, especially if you have carpentry skills and access to the necessary tools and materials. Making your own windows allows for customization to fit specific dimensions or styles not readily available in pre-made options. However, it's important to note that creating energy-efficient, durable windows that meet building codes can be challenging. For double-glazed or specialized windows, professional manufacturing processes might be necessary to achieve the desired performance and safety standards.
How do we make windows?
Window manufacturing involves several steps, depending on the type of window (e.g., single-pane, double-glazed) and the materials used (e.g., wood, vinyl, aluminum). Here's a simplified overview:
- Design and Measurements: Start with detailed designs and measurements to ensure the window fits its intended space and meets any specific functional requirements.
- Frame Construction: The window frame is constructed from the chosen material. Wood frames are typically cut and assembled, while vinyl or aluminum frames might be extruded into the correct shape and size.
- Glass Cutting: Glass is cut to size according to the frame's dimensions. For double-glazed windows, two glass panes are cut.
- Assembly: For single-pane windows, the glass is installed into the frame and secured with glazing points and putty or sealant. Double-glazed windows involve sealing two panes of glass with a spacer between them, creating an insulating air gap. The assembled unit is then placed into the frame.
- Finishing: The window is finished with any necessary hardware (e.g., locks, handles) and, if applicable, painted or sealed to protect against the elements.
How are windows made?
Windows are made using a combination of manual craftsmanship and automated machinery, especially in commercial manufacturing. The process typically includes:
- Frame fabrication: Based on the chosen material, frames are either welded (for materials like vinyl or aluminum) or joined (for wood).
- Glass production: Glass panes are cut to size and, if making double or triple-glazed windows, assembled with spacers and filled with inert gas for insulation.
- Assembly: The glass and frame are assembled, with seals and gaskets added to enhance insulation and waterproofing.
- Quality check: Finished windows undergo quality checks for durability, insulation, and functionality.
Making windows, particularly for specific or custom applications, requires attention to detail and precision to ensure they are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Whether for a DIY project or understanding commercial production, knowledge of these processes can inform better decision-making for your window needs.
Window Costs and Materials
Understanding the cost factors and material choices for windows is crucial for anyone planning to install or replace windows. This section delves into commonly asked questions about window costs and materials, providing insights that can help guide your decisions. We’ve also added more questions to cover a broader range of concerns related to window costs and the materials used in their construction.
What type of window is the most expensive?
The cost of windows can vary widely based on type, material, and features. Typically, custom and large-scale windows like bay, bow, or custom-shaped windows tend to be the most expensive due to their complexity, size, and the labor involved in installation. High-performance windows with special coatings for energy efficiency or sound insulation can also add to the cost.
Are bigger windows more expensive?
Yes, larger windows generally cost more than smaller ones. The price increase is due to the need for more materials, such as glass and frame materials, and the complexity of installation. Additionally, larger windows may require special reinforcement or framing considerations, further increasing the cost.
What color windows are most expensive?
Window color can affect cost, especially for materials like vinyl or aluminum, which come in standard and custom colors. Custom colors or finishes often come at a premium. Historically, darker colors like black or specific shades of grey might be more expensive due to the specialized materials or processes needed to achieve those colors and ensure they resist fading over time.
Should I buy expensive windows?
Investing in high-quality, more expensive windows can be worthwhile for several reasons, including better energy efficiency, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Expensive windows often come with advanced features like improved insulation, UV protection, and custom designs that can enhance your home's value and reduce energy bills over time. However, it’s important to balance cost with your specific needs and budget.
Why are black windows so expensive?
Black windows are often more expensive because the dark color may require specialized coatings or treatments to ensure long-term durability and resistance to fading. The process to maintain color integrity and performance in darker windows can add to the manufacturing costs.
Why are grey windows more expensive?
Similar to black windows, grey windows can be more expensive due to the additional processes required to achieve and maintain the specific shade. Ensuring the color remains consistent and resistant to weathering or sunlight can involve advanced materials and treatments.
Which windows are more expensive?
In addition to large and custom-shaped windows, windows with specialized glass (e.g., triple-glazing, low-E coatings) or frames made from premium materials like fiberglass or composite are typically more expensive. Features aimed at enhancing energy efficiency, sound insulation, or security can also increase the cost.
What is the cheapest window design?
The cheapest window designs are usually standard-size, single-hung, or double-hung windows made from more affordable materials like vinyl. These windows are mass-produced, making them more cost-effective for both purchase and installation.
What is the best material for window frames?
The best material for window frames depends on your needs for durability, maintenance, insulation, and budget. Here's a quick overview:
- Vinyl: Affordable, good insulation, low maintenance, but may not be as strong or durable as other materials.
- Wood: Excellent insulation and aesthetics, but requires more maintenance and is susceptible to moisture and insects.
- Aluminum: Strong and low maintenance, but conducts heat, potentially reducing energy efficiency unless it includes a thermal break.
- Fiberglass: Strong, durable, low maintenance, and offers good insulation; tends to be more expensive but can be a cost-effective investment over time.
- Composite: Combines materials to offer strength, durability, and insulation, with low maintenance needs; can be mid-range to expensive.
How does the glazing type affect window costs?
The type of glazing significantly affects window costs due to the different materials and technologies used. Single-glazed windows are the least expensive but offer the least insulation. Double-glazed windows, with two panes of glass and an insulating air or gas fill between them, are more costly but provide better insulation and energy efficiency. Triple-glazed windows, which have three panes of glass, offer the highest level of insulation but also come with a higher price tag due to the additional materials and complexity of construction. Specialty coatings, such as low-emissivity (low-E) coatings, can add to the cost but improve energy efficiency by reflecting heat while letting light in.
Are energy-efficient windows worth the higher initial cost?
Yes, energy-efficient windows are often worth the higher initial cost for several reasons. First, they can significantly reduce energy bills by keeping your home warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer, thanks to improved insulation. This means less energy is needed for heating and cooling, leading to long-term savings. Second, they can improve the comfort of your home by reducing drafts and cold spots. Third, energy-efficient windows can also protect furnishings by reducing UV exposure, which can fade fabrics and carpets. Lastly, they may increase your home’s resale value by making it more appealing to buyers looking for energy-efficient features.
What are the long-term savings associated with high-quality window materials?
High-quality window materials can lead to significant long-term savings in several ways. Durable materials like fiberglass or composite reduce the need for replacements and repairs over the window's life, saving money on maintenance costs. Energy-efficient materials and designs can drastically cut heating and cooling costs by improving your home's insulation. Additionally, high-quality windows can enhance the overall value of your home, making it more attractive to potential buyers if you decide to sell. The exact savings will depend on factors like your climate, energy prices, and the specific window technologies you choose.
How do material choices impact window lifespan and maintenance needs?
Material choices have a direct impact on both the lifespan and maintenance needs of windows. Wood frames offer a classic aesthetic but require regular painting or staining to prevent decay and warping. Vinyl frames are low maintenance and reasonably durable but may become brittle and fade over time, especially in harsh weather conditions. Aluminum frames are strong and require little maintenance but are prone to condensation and heat transfer. Fiberglass frames are among the most durable and maintenance-free options, resistant to warping, fading, and cracking, and offer excellent insulation. Composite frames combine the benefits of multiple materials, often resulting in a durable, low-maintenance window with good insulation properties. Choosing the right material based on your climate, the window's exposure, and your willingness to perform maintenance can significantly affect the window's performance and longevity.
Can choosing certain window materials improve home security?
Yes, choosing certain window materials can improve home security. Frames made from strong, durable materials like aluminum or fiberglass are harder to force open or damage, providing an extra layer of security. Windows that feature laminated or tempered glass are also more resistant to breaking, making it more difficult for intruders to enter through them. Additionally, windows can be equipped with locks, reinforced glass, and other security features to enhance protection. When selecting windows, considering security features and materials that offer a balance between aesthetic appeal, energy efficiency, and security can make your home safer.
Window Design and Efficiency
The design and efficiency of windows play a crucial role in the comfort, energy consumption, and aesthetics of a home. This section covers key questions related to these aspects, providing insights into how window size, shape, and placement can impact overall building performance and livability.
Are bigger windows better?
Bigger windows offer more natural light and can enhance views, making spaces feel larger and more connected to the outdoors. However, they also have downsides, such as potential energy loss, higher costs, and privacy concerns. The "better" aspect depends on specific goals: maximizing light and views or improving energy efficiency and privacy. It's essential to balance size with these factors, considering climate, orientation, and window technology (e.g., glazing options) to ensure they meet your needs effectively.
What is the most efficient window shape?
The most efficient window shape for energy performance tends to be rectangular with a higher vertical orientation. This shape allows for optimal daylighting while minimizing heat loss and gain, compared to more complex shapes that might have more surface area or less efficient sealing. However, efficiency also heavily depends on other factors like glazing type, frame material, and installation quality. When considering window shape, it's also vital to think about architectural style and how the window serves the space it's in, balancing efficiency with design and functionality.
How do high-performance windows work?
High-performance windows improve comfort and energy efficiency through several key features:
- Multiple Glass Panes: Double or triple glazing traps air or inert gas between the panes, reducing heat transfer.
- Low-E Coatings: These microscopic metallic coatings reflect infrared light, keeping heat inside during winter and outside during summer, without significantly reducing visible light.
- Warm Edge Spacers: These spacers between glass panes reduce heat transfer and prevent condensation around the window edges.
- Improved Frame Materials: Frames made from materials like fiberglass, vinyl, or treated wood offer better insulation and durability. Together, these features reduce energy loss, protect against UV light, decrease noise, and enhance the overall comfort of a building.
What is design windows?
Designing windows involves considering aesthetic, functional, and energy efficiency aspects to select and position windows in a way that meets the building's needs. This includes choosing the right size, shape, material, and type of window (e.g., fixed, operable) while also considering the window's orientation, the climate, and how it integrates with the building's design. Effective window design enhances natural light, ventilation, and views, contributing to a comfortable and sustainable living environment.
How do you design window placement?
Designing window placement involves:
- Maximizing Natural Light: Positioning windows to capture daylight, considering the sun's path and the building's orientation.
- Enhancing Views and Aesthetics: Aligning windows with desirable views and the building's architectural style.
- Improving Ventilation: Placing operable windows to promote cross-ventilation.
- Considering Privacy: Placing windows to offer views and light while maintaining privacy from neighbors and passersby.
- Energy Efficiency: Using windows' location and size to minimize energy loss and leverage passive solar heating or cooling when appropriate.
How far from the floor should windows be?
The distance from the floor to the bottom of a window can vary based on the window's purpose, the room's function, and building codes. Generally, a height of about 3 feet (90 cm) from the floor to the bottom of the window is common for residential buildings, providing a balance between views, natural light, and furniture placement. However, floor-to-ceiling windows or windows designed for specific views might have different requirements.
Where not to put windows?
Avoid placing windows:
- In direct alignment with neighbors' windows, to maintain privacy.
- Where furniture or other functional elements obstruct them, limiting their utility and aesthetic value.
- In locations with excessive direct sunlight without proper shading, which can lead to overheating and discomfort.
- Where they compromise structural integrity, especially without proper engineering support.
- In areas prone to high wind or water exposure without using appropriate protective measures or window types. Designing window placement with these considerations in mind ensures functionality, comfort, and energy efficiency while enhancing the building's overall design.
Window Preferences and Choices
Choosing the right windows for your home involves considering factors such as cost, design, light requirements, and energy efficiency. This section addresses common questions about window preferences and choices, helping you make informed decisions to suit your specific needs.
Which window is more expensive?
Custom-designed windows, large floor-to-ceiling windows, and those with advanced energy-efficient technologies like triple glazing or specialized coatings tend to be more expensive. Material choice also plays a significant role, with wooden and fiberglass frames generally costing more than vinyl.
What do you call 3 windows together?
Three windows installed together are commonly referred to as a "bay window." Typically, a bay window extends outward from the main walls of a building and forms a bay in a room, offering wide views and additional light.
Which window is brightest in house?
The brightest window in a house is usually a large, south-facing window (in the northern hemisphere) without obstructions. South-facing windows receive the most amount of daylight throughout the year, maximizing natural light.
What windows are best for lighting?
Windows that are best for lighting include large, unobstructed windows, especially those facing towards the south in the northern hemisphere (and north in the southern hemisphere). Skylights and clerestory windows are also excellent for providing consistent, natural light without compromising privacy or wall space.
Why use clerestory windows?
Clerestory windows are used for several reasons:
- Natural Light: They allow abundant natural light to enter a space from above, which can illuminate deeper into the interior than wall-mounted windows.
- Privacy: Positioned high on the wall, they provide light without compromising privacy.
- Ventilation: When operable, they can enhance ventilation, allowing hot air to escape and cooler air to circulate.
- Aesthetic: Architecturally, they add interest and can create a feeling of space and height in a room.
Which windows are most popular?
The most popular windows vary by region and architectural style but typically include double-hung, casement, and sliding windows due to their versatility, ease of use, and the balance of light, ventilation, and efficiency they offer.
Who makes the best windows?
The "best" window manufacturers depend on specific needs, including style, material, energy efficiency, and budget. Well-regarded brands include Andersen, Pella, and Milgard, among others, known for their quality, range of options, and customer service.
Which windows are best for a house?
The best windows for a house depend on the house's design, climate, orientation, and the homeowner's preferences. Energy-efficient windows with good insulation properties, like double or triple-glazed windows with low-E coatings, are generally recommended for most homes.
Which windows get hottest?
Windows that get the hottest are typically west-facing windows due to the intense afternoon sun, followed by east-facing windows which catch the morning sun. Windows without shading or energy-efficient coatings can significantly increase indoor temperatures.
What is a large French window?
A large French window refers to a tall, wide window that extends to the floor and can function as a door. They are essentially large French doors without a central mullion, offering unobstructed views and access to the outside.
What is the best quality of window glass?
The best quality of window glass for residential use often includes features like double or triple glazing, low-emissivity (low-E) coatings, and inert gas fillings like argon or krypton to improve thermal performance and reduce energy transfer.
What is the best window made of?
The best window material depends on your priorities, such as aesthetic, thermal performance, maintenance, and durability. Wood offers natural beauty but requires maintenance, while vinyl provides good insulation and is low maintenance. Fiberglass and composite materials offer a balance of durability, low maintenance, and good thermal insulation.
Which window is the brightest?
The brightest windows are typically those without shades or curtains and are made of clear, unobstructed glass, allowing maximum light transmission. Large windows facing the equator (south in the northern hemisphere, north in the southern hemisphere) usually provide the most brightness.
What type of window lets in the most light?
Fixed windows (windows that don't open) with minimal framing and clear glass allow in the most light because there are no obstructions or operational components to block the sunlight. Large picture windows are a common example.
What are natural light windows called?
Windows designed specifically to maximize natural light are often called "daylighting windows," which can include skylights, clerestory windows, and large picture windows. These windows aim to provide ample natural light, reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day.
How do window frames affect the overall look of a house?
Window frames significantly influence a house's aesthetic appeal and architectural coherence. The material, color, and design of window frames can complement the home's style—be it modern, traditional, or something in between. For example, sleek, minimalist frames may enhance a contemporary home, while ornate wooden frames can add warmth to a traditional design. Choosing the right frames can tie the exterior elements together, boosting curb appeal.
Can windows improve indoor air quality?
Yes, windows can improve indoor air quality by providing natural ventilation, which allows fresh air to enter and stale, polluted air to exit a home. Operable windows, like casement or sliding windows, are particularly effective for this purpose. Strategic placement of these windows can facilitate cross-ventilation, ensuring a constant flow of fresh air and helping to remove indoor air pollutants.
What are the benefits of triple-glazed windows over double-glazed?
Triple-glazed windows offer several benefits over double-glazed, including:
- Improved Energy Efficiency: The additional glass pane and gas layer provide better insulation, reducing heat transfer. This means warmer interiors in winter and cooler in summer, leading to lower energy bills.
- Enhanced Comfort: Triple glazing reduces cold spots and drafts near windows, contributing to a more consistent indoor temperature.
- Noise Reduction: The extra layer of glass and gas significantly reduces noise from outside, making them ideal for homes in noisy areas.
- Increased Security: The additional pane makes these windows tougher to break, enhancing home security.
While triple-glazed windows offer superior performance, they also come with a higher initial cost and may have a heavier frame to support the extra weight, which should be considered in the decision-making process.
How does window orientation affect energy efficiency?
Window orientation significantly impacts a home's energy efficiency and comfort. In the northern hemisphere:
- South-facing windows capture the most sunlight, especially in winter, contributing to natural heating. However, they may require shading in summer to prevent overheating.
- North-facing windows receive less sunlight, making them cooler and ideal for consistent, natural light with minimal glare.
- East-facing windows catch the morning sun, warming spaces quickly but can be cooler in the afternoon and evening.
- West-facing windows are exposed to intense afternoon and evening sun, which can cause overheating in summer months. Selecting the right type of window and treatments (like blinds or awnings) based on orientation can enhance a home's energy efficiency and comfort.
What window treatments are best for energy efficiency?
Energy-efficient window treatments can significantly reduce heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Some of the best options include:
- Cellular shades: Their honeycomb design traps air, providing insulation.
- Thermal curtains: Heavy fabrics or those with a thermal lining help block heat transfer.
- Shutters: Both interior and exterior shutters add an extra layer of insulation.
- Reflective films: These can reduce heat gain in summer by reflecting sunlight away from the window. Choosing the right window treatments based on your climate and the window's orientation can complement the window's built-in energy-efficient features for optimal performance.
How can smart windows change home design?
Smart windows, equipped with technologies like electrochromic glass, can automatically or manually adjust their tint to control sunlight, glare, and heat entering a home. This capability can revolutionize home design by:
- Reducing the need for window treatments: Smart windows eliminate the need for blinds or curtains for light control, offering unobstructed views and sleek design options.
- Improving energy efficiency: By optimizing the amount of light and heat entering a space, smart windows can significantly reduce reliance on artificial lighting and climate control systems.
- Enhancing comfort: Smart windows can instantly adapt to changing outdoor conditions, maintaining a comfortable indoor environment without manual adjustments. As smart window technology continues to evolve, it's likely to become a more integral part of modern, energy-efficient, and automated home design.
Miscellaneous Window Questions
This section tackles a variety of questions about windows, ranging from terminology and technology to history and durability. These answers aim to clarify some less commonly discussed aspects of windows.
What are style line windows?
Style line windows refer to a specific design of window that features a slim frame, maximizing the glass area for a clean, modern look. They are often used in contemporary architecture to provide expansive views and increase natural light while maintaining a sleek and minimalistic design aesthetic. The reduced frame size doesn't mean a compromise in performance; these windows can still offer excellent energy efficiency and functionality.
Which Windows is faster?
If this question refers to Microsoft Windows operating systems, the speed can vary based on several factors, including the version of Windows, the hardware it's running on, and the tasks it's performing. Generally, newer versions of Windows are designed to be more efficient and make better use of modern hardware, potentially offering faster performance in comparison to older versions. For instance, Windows 10 is often considered faster and more efficient than its predecessors due to optimizations and updates.
Which Windows last longer?
In terms of window materials, durability and lifespan vary. Fiberglass windows are known for their long lifespan, often lasting 50 years or more due to their resistance to warping, rotting, and corrosion. Vinyl windows also offer a considerable lifespan, typically around 20-40 years, with minimal maintenance. Wood windows, while offering a classic aesthetic, may require more maintenance and potentially have a shorter lifespan if not properly maintained due to vulnerability to moisture and insects.
Why are Windows called Windows?
The term "windows" for the graphical user interface elements on a computer screen comes from the metaphor of a window in a building. Just as a physical window offers a view into or out of a building, a computer window offers a view into the software application it represents. This metaphor helps users understand the concept of viewing and interacting with multiple applications or documents simultaneously. The naming convention was popularized with the release of Microsoft Windows in the mid-1980s, which brought this graphical user interface concept to a wider audience.
How many styles of windows are there?
There are numerous styles of windows, each with its characteristics and uses. Some of the most common include:
- Double-Hung Windows: Have two sashes that move up and down.
- Casement Windows: Hinged at the sides and open outward.
- Awning Windows: Hinged at the top and open outward.
- Sliding Windows: Have one or more sashes that slide horizontally.
- Bay and Bow Windows: Extend outward from the home's exterior, creating a curved appearance for bow windows and a more angular appearance for bay windows.
- Picture Windows: Large, fixed windows designed to provide a clear view.
- Skylights: Installed in the roof to allow light to enter from above.
- Garden Windows: Extend outward and provide a space that can be used for plants. The choice among these and other styles depends on architectural preference, functionality, and the specific needs of the space, such as light, ventilation, and aesthetics.
Additional Related Questions
Exploring various aspects of windows can help enhance the functionality, efficiency, and aesthetic appeal of a home. These additional questions delve into insulation, design trends, noise reduction, and more to provide comprehensive insights.
How can windows improve home insulation?
Windows can significantly improve home insulation through several key features:
- Double or Triple Glazing: Multiple layers of glass with air or gas-filled spaces between them reduce heat transfer.
- Low-E Coatings: These coatings reflect infrared light, keeping heat inside in winter and outside in summer, without blocking natural light.
- Warm Edge Spacers: These reduce heat transfer at the edge of glass panes, where condensation often forms.
- Proper Installation: Ensuring windows are correctly installed to prevent air leaks is crucial for maintaining insulation. By upgrading to energy-efficient windows with these features, you can improve your home's insulation, resulting in lower energy bills and increased comfort.
What are the latest trends in window design?
Recent trends in window design include:
- Slim Frames and Large Panes: Maximizing natural light and views with minimalistic frames.
- Energy Efficiency: Advanced technologies for better insulation and solar heat gain control.
- Smart Windows: Windows that tint automatically in response to sunlight or can be controlled for privacy and light.
- Sustainable Materials: Increasing use of eco-friendly materials that offer durability and low environmental impact.
- Custom Shapes and Styles: Unique windows that serve as focal points or complement specific architectural styles. These trends reflect a shift towards sustainability, functionality, and aesthetic flexibility in modern homes.
How does window orientation affect energy efficiency?
Window orientation plays a critical role in energy efficiency by influencing solar heat gain and natural light:
- North-facing windows (in the northern hemisphere) provide steady, natural light with minimal direct sun, reducing cooling needs.
- South-facing windows allow for maximum solar heat gain in winter, reducing heating costs, but may require shading in summer to prevent overheating.
- East-facing windows receive morning sun, warming the space early in the day.
- West-facing windows get intense afternoon and evening sun, often requiring shading to manage heat gain and glare. Strategically placing windows based on orientation can leverage natural light and heat to improve a home's energy efficiency and comfort.
Can windows be designed to reduce noise from outside?
Yes, windows can be designed to reduce exterior noise through:
- Double or Triple Glazing: The air or gas layers between panes act as sound barriers.
- Thicker Glass: Heavier glass panes can block more sound.
- Laminated Glass: A layer of plastic between glass panes dampens sound vibrations.
- Tight Seals: Properly sealed windows prevent sound from entering through gaps. Choosing windows with these features can significantly reduce noise, enhancing indoor comfort in noisy environments.
What are the safety considerations when installing large windows?
Safety considerations for large windows include:
- Tempered Glass: This glass type shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing injury risk.
- Laminated Glass: Holds together when broken, preventing shards from falling.
- Proper Framing and Support: Ensuring the structure can support the window's weight and resist wind loads.
- Guardrails or Opening Restrictions: For windows that present a fall risk, especially in upper stories.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Compliance with local codes that may dictate size, height, and type of glass for safety. Considering these factors during installation can enhance safety while enjoying the benefits of large windows.
How does the frame material affect a window's performance and appearance?
The frame material impacts a window's durability, maintenance needs, thermal insulation, and aesthetic:
- Wood: Offers natural beauty and good insulation but requires maintenance to prevent decay.
- Vinyl: Low maintenance and good insulation but may have limited color and style options.
- Aluminum: Durable and low maintenance but conducts heat, affecting thermal performance.
- Fiberglass: Excellent durability, insulation, and can be painted; generally more expensive.
- Composite: Combines materials for strength, low maintenance, and insulation; can mimic the appearance of wood. Choosing the right frame material involves balancing these factors to meet specific performance and design goals.
What advancements in glass technology are most beneficial for residential windows?
Advancements in glass technology that benefit residential windows include:
- Low-E Coatings: Improve energy efficiency by reflecting heat while letting light through.
- Dynamic Glazing: Allows windows to change tint automatically or on demand to control light and heat.
- Triple Glazing: Offers superior insulation and noise reduction compared to double glazing.
- Laminated Glass: Provides safety, security, and sound insulation by holding glass layers together if broken.
- Gas Fills: Argon or krypton gas between panes for better thermal insulation than air. These technologies enhance comfort, efficiency, and safety, making modern windows more effective and versatile.
How to select windows for historical or traditional homes without compromising modern efficiency standards?
Selecting windows for historical or traditional homes involves:
- Matching Aesthetics: Choosing windows that mimic the original style and materials as closely as possible.
- Advanced Materials: Opting for modern materials (like treated wood or composite frames) that offer historical looks with improved performance.
- Energy-Efficient Glazing: Using double or triple-glazed units with low-E coatings and inert gas fills that look traditional but provide modern insulation.
- Custom Solutions: Working with manufacturers that offer custom shapes and sizes to fit historical profiles.
- Preservation and Retrofitting: Where possible, preserving original frames and retrofitting them with energy-efficient glazing. These approaches allow homeowners to maintain the historical charm of their homes while enjoying the benefits of modern window technology.
Explore Further: Expansive Windows
Learn more about the transformative power of expansive windows in modern architecture and interior design. This section dives into a variety of closely and generally related topics, offering you a path to deepen your understanding and appreciation of expansive windows and their impact on spaces and occupants alike.
Design and Aesthetics
The Role of Windows in Modern Architecture
Discover how expansive windows shape the character of contemporary buildings, influencing both their exterior appeal and interior ambiance.
Expansive Windows and Interior Design
Explore how large windows can be used creatively in interior design to enhance natural light, views, and the perception of space.
Technology and Innovation
Advances in Glass Technology
Learn about the technological breakthroughs that have made expansive windows more practical, including improvements in energy efficiency, strength, and clarity.
Smart Glass and Automated Systems
Dive into the world of smart glass and how it’s being used in expansive windows for privacy, energy conservation, and climate control within homes and offices.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Expansive Windows and Green Building Design
Understand the role of large windows in sustainable architecture, including strategies for maximizing light while minimizing heat loss and gain.
Thermal Performance of Large Windows
Explore how the thermal performance of expansive windows is measured and improved, ensuring comfortable interiors across seasons.
Planning and Installation
Architectural Planning for Expansive Windows
Get insights into the architectural planning process for integrating large windows into buildings, considering factors like orientation, shading, and structural support.
DIY Installation Tips for Large Windows
Learn the basics of installing expansive windows yourself, including tips on handling, framing, and sealing to ensure durability and performance.
Historical Context
Evolution of Window Design
Trace the evolution of window design throughout history, with a focus on how and why expansive windows have become a hallmark of modern buildings.
Iconic Buildings with Expansive Windows
Study examples of iconic buildings that have used expansive windows in revolutionary ways, setting new standards for design and functionality.
By exploring these topics, you'll gain a deeper understanding of the complexities and possibilities presented by expansive windows in architecture. Whether you’re a professional in the field, a student of design, or simply someone with an interest in the aesthetics and practicality of modern buildings, there’s much to learn and appreciate about the role of windows in shaping our environments.
